The problem:
- TMD is a painful condition effecting one or both of the jaw joints (TMJ).
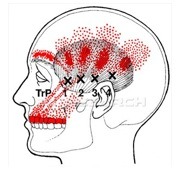
- Pain is generated through inflammation and irritation of the joint capsule and/or the disc and may involve painful trigger points in the muscles around the joint.
- Headaches and neck pain are also common features of this condition.
- TMD is commonly caused through clenching and grinding of the teeth, often in response to stress, or may be a result of poor co-ordination of the muscles of the jaw.
Interesting facts:
- The TMJ should be under compression for 18 mins per day, in clenchers and grinders this can often be greater than 2 hours!
- As stress is often a trigger for development of the condition, stress management to decrease parafunctional habits is important.
What you can expect/look out for:
- Clenching and grinding can start to wear the teeth and may require the use of a splint to protect the teeth and decrease the wear on the TMJ.
- The TMJ is a very small but sensitive joint, exercises and tissue release should be fairly gentle.
- Hard and chewy foods should be avoided.
Management suggestions:
- The first stage in management is to release the tight and painful tissue around the joint.
- Heat and self-massage to sensitive areas can be quite effective.
- Anti inflammatory medication can be effective in settling symptoms associated with TMD (consult your GP).
- Identifying and trying to avoid aggravating activities is important in allowing the painful tissue to settle.
- Quite often clenching and grinding can take place at night. Exercise before going to sleep, this releases endorphins which can help reduce stress levels which has been shown to trigger these habits.
At Sydney Physiotherapy Solutions our highly qualified physiotherapists specialise in the assessment, treatment and prevention of neuromusculoskeletal injuries.
Contact us today – 9252 5770
This handout was prepared by Sydney Physiotherapy Solutions and is intended as a general information service. Please note that the information provided is not intended as a substitute for advice from a registered physician or healthcare professional. If symptoms persist, please consult your doctor.